问题描述
我有一个使用多个窗口的应用程序。如何快速将该应用程序的所有窗口调到前台?
当我使用 scroll-wheel 滚动浏览应用程序时,它只显示一个窗口。当转到下一个窗口时,最后一个窗口将再次进入后台。
当我单击应用程序图标时,我会获得所有窗口的全屏概览。我必须手动选择每个窗口并将鼠标移过半个屏幕几次。
到目前为止,我最好的解决方案是最小化所有窗口( Ctrl + Super + D ),然后使用 scroll-wheel 显示我的应用程序的窗口。
有更好的解决方案吗?
最佳回答
编辑-新答案-
下面的答案仍然完全有效,因此建议的选项也是如此。然而,持续的洞察让我添加了这个选项来使用下面的指标,这可能是最优雅的解决方案。
因此,它可能应该取代选项 5(使用 .desktop 文件)。
只需从列表中选择应用程序,相应应用程序的所有窗口(当前视口上存在)就会出现:
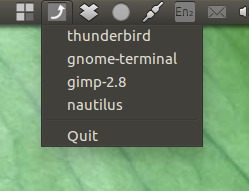
如何使用
来自 ppa:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:vlijm/upfront
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install upfront
…或手动:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import signal
import gi
gi.require_version('Gtk', '3.0')
gi.require_version('AppIndicator3', '0.1')
from gi.repository import Gtk, AppIndicator3, GObject
import time
from threading import Thread
import os
import subprocess
import getpass
currpath = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
class Indicator():
def __init__(self):
self.app = 'raise_apps'
iconpath = os.path.join(currpath, "raise.png")
self.indicator = AppIndicator3.Indicator.new(
self.app, iconpath,
AppIndicator3.IndicatorCategory.OTHER)
self.indicator.set_status(AppIndicator3.IndicatorStatus.ACTIVE)
self.indicator.set_menu(self.create_menu())
# the thread:
self.update = Thread(target=self.check_recent)
# daemonize the thread to make the indicator stopable
self.update.setDaemon(True)
self.update.start()
def create_menu(self):
# creates the (initial) menu
self.menu = Gtk.Menu()
# separator
initial = Gtk.MenuItem("Fetching list...")
menu_sep = Gtk.SeparatorMenuItem()
self.menu.append(initial)
self.menu.append(menu_sep)
# item_quit.show()
self.menu.show_all()
return self.menu
def raise_wins(self, *args):
index = self.menu.get_children().index(self.menu.get_active())
selection = self.menu_items2[index][1]
for w in selection:
execute(["wmctrl", "-ia", w])
def set_new(self):
# update the list, appearing in the menu
for i in self.menu.get_children():
self.menu.remove(i)
for app in self.menu_items2:
sub = Gtk.MenuItem(app[0])
self.menu.append(sub)
sub.connect('activate', self.raise_wins)
# separator
menu_sep = Gtk.SeparatorMenuItem()
self.menu.append(menu_sep)
# quit
item_quit = Gtk.MenuItem('Quit')
item_quit.connect('activate', self.stop)
self.menu.append(item_quit)
self.menu.show_all()
def get_apps(self):
# calculate screen resolution
res_output = get("xrandr").split(); idf = res_output.index("current")
res = (int(res_output[idf+1]), int(res_output[idf+3].replace(",", "")))
# creating window list on current viewport / id's / application names
w_data = [l.split() for l in get(["wmctrl", "-lpG"]).splitlines()]
# windows on current viewport
relevant = [w for w in w_data if 0 < int(w[3]) < res[0] and 0 < int(w[4]) < res[1]]
# pids
pids = [l.split() for l in get(["ps", "-u", getpass.getuser()]).splitlines()]
matches = [[p[-1], [w[0] for w in relevant if w[2] == p[0]]] for p in pids]
return [m for m in matches if m[1]]
def check_recent(self):
self.menu_items1 = []
while True:
time.sleep(4)
self.menu_items2 = self.get_apps()
for app in self.menu_items2:
app[0] = "gnome-terminal" if "gnome-terminal" in app[0] else app[0]
if self.menu_items2 != self.menu_items1:
GObject.idle_add(
self.set_new,
priority=GObject.PRIORITY_DEFAULT
)
self.menu_items1 = self.menu_items2
def stop(self, source):
Gtk.main_quit()
def get(command):
return subprocess.check_output(command).decode("utf-8")
def execute(command):
subprocess.Popen(command)
Indicator()
GObject.threads_init()
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, signal.SIG_DFL)
Gtk.main()
-
该指标需要
wmctrl\n
sudo apt-get wmctrl\n -
将指标复制到空文件中,另存为
raise_apps.py -
复制下面的图像,将其精确命名为
raise.png并保存在与指标相同的目录中。\n
-
然后只需通过命令运行它:\npython3 /path/to/raise_apps.py
-
如果要启动应用程序,请添加:
\n
/bin/bash -c "sleep 10 && python3 /path/to/raise_apps.py" \n
旧答案:
关于问题
使用正确的工具,”just” 提升应用程序的所有窗口并不是很复杂。确保仅当前视口的窗口升起有点复杂。然而,真正的挑战是找到一种方便的方法来使用户可以执行该操作。
下面五个选项可以解决这个问题,展示如何做到这一点。所有选项均已准备好可供使用。然而,最后一个选择是一种实验性的选择。它工作正常,但有一些小的外观缺点,如选项描述中所述。尽管如此,我还是把它作为一个概念添加了进来。
正如评论中所建议的那样,以不重叠的方式自动展开窗口对我来说似乎不是一个实际的想法;如果您在 (application-wise) 分组窗口设置中工作,脚本可能会意外地重新排列窗口。
如何使用
对于所有选项,您需要:
-
如果您的系统上尚未安装
wmctrl:\n
sudo apt-get install wmctrl\n -
创建目录(如果尚不存在):
\n
~/bin\n\n
(说明:目录
~/bin位于 $PATH 中,因此您可以通过其名称运行可执行文件) -
复制该选项对应的脚本,粘贴到一个空文件中,在
~/bin中另存为raise_app(无扩展名)并使其可执行
在单独的选项中,将解释可能的附加步骤。
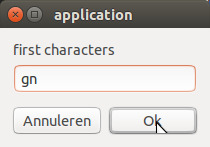
选项 1:通过输入一个或多个字符来选择应用程序
-
按组合键,会出现
zenity窗口 -
在输入框中输入应用程序名称的一个或多个字符
-
按回车键
这将使匹配应用程序的所有窗口(在当前视口上)出现在前面。
提升当前视口上的所有 gnome-terminal 窗口:
如何使用:
-
按照“如何使用”中的说明进行设置
-
Test-run 通过命令:
\n
raise_app\n -
如果一切正常,请将其添加到您选择的快捷键组合中:选择:系统设置> “Keyboard”> “Shortcuts”> “Custom Shortcuts”。单击 “+” 并添加命令
剧本:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import subprocess
import getpass
def get(command):
return subprocess.check_output(["/bin/bash", "-c", command]).decode("utf-8")
def execute(command):
subprocess.Popen(["/bin/bash", "-c", command])
# calculate screen resolution
res_output = get("xrandr").split(); idf = res_output.index("current")
res = (int(res_output[idf+1]), int(res_output[idf+3].replace(",", "")))
# creating window list on current viewport / id's / application names
w_data = [l.split()[0:7] for l in get("wmctrl -lpG").splitlines()]
windows = [[get("ps -u "+getpass.getuser()+" | grep "+w[2]).split()[-1], w[0]]
for w in w_data if 0 < int(w[3]) < res[0] and 0 < int(w[4]) < res[1]]
# ask user for first characters
try:
arg = get('zenity --entry --text "first characters" --title "application"').strip()
except subprocess.CalledProcessError:
pass
# raise matching windows
try:
[execute("wmctrl -ia "+item[1]) for item in windows if item[0].startswith(arg)]
except (subprocess.CalledProcessError, NameError):
pass
选项 2:循环浏览应用程序并使用组合键升起窗口:
假设我在组合键 Alt + 1 下有以下脚本。我打开了几个窗口:
-
火狐浏览器
-
gnome-terminal
-
nautilus
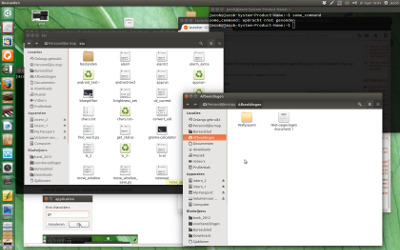
目前状态:
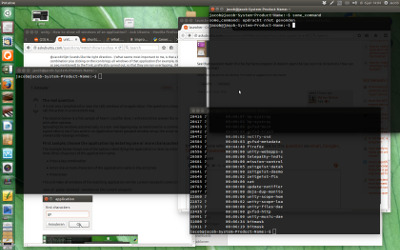
我按一次 Alt + 1 ,所有 nautilus 窗口都会升起:
我再次按下 Alt + 1 ,所有 firefox 窗口都会升起:
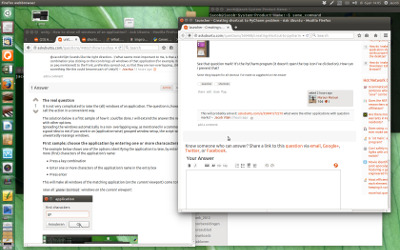
我再次按下 Alt + 1 ,所有 gnome-terminal 窗口再次升起,循环重新开始:

如何使用
-
按照“如何使用”中的说明进行设置
-
将其添加到您选择的快捷键组合中:选择:系统设置> “Keyboard”> “Shortcuts”> “Custom Shortcuts”。单击 “+” 并添加命令
\n
raise_app\n
然后使用组合键在分组的应用程序窗口中循环浏览您的应用程序。
剧本:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import subprocess
import getpass
include_single = True # set to False if you only want to cycle through apps with multiple windows
def get(command):
return subprocess.check_output(["/bin/bash", "-c", command]).decode("utf-8")
def execute(command):
subprocess.Popen(["/bin/bash", "-c", command])
def get_frontmost():
cmd = "xprop -root"
frontmost = [l for l in get(cmd).splitlines() if\
"ACTIVE_WINDOW(WINDOW)" in l][0].split()[-1]
return frontmost[:2]+"0"+frontmost[2:]
# calculate screen resolution
res_output = get("xrandr").split(); idf = res_output.index("current")
res = (int(res_output[idf+1]), int(res_output[idf+3].replace(",", "")))
# creating window list on current viewport / id's / application names
w_data = [l.split()[0:7] for l in get("wmctrl -lpG").splitlines()]
windows = [[get("ps -u "+getpass.getuser()+" | grep "+w[2]).split()[-1], w[0]]
for w in w_data if 0 < int(w[3]) < res[0] and 0 < int(w[4]) < res[1]]
# create application list to cycle through
if include_single == False:
pre = [it[0] for it in windows]
apps = sorted(list(set([it for it in pre if pre.count(it) > 1])))
else:
apps = sorted(list(set([it[0] for it in windows])))
if len(apps) == 0:
pass
else:
# get the frontmost window as a last itm in the cycle
front = get_frontmost()
front_pid = [l.split()[2] for l in get("wmctrl -lp").splitlines() if front in l][0]
last_infront = get("ps -u "+getpass.getuser()+" | grep "+front_pid).split()[-1]
# determine next apllication to raise
if not last_infront in apps or last_infront == apps[-1]:
arg = apps[0]
print(arg)
else:
arg = apps[apps.index(last_infront)+1]
# raise matching windows
try:
[execute("wmctrl -ia "+item[1]) for item in windows if item[0] == arg]
except (subprocess.CalledProcessError, NameError):
pass
选项 3:按下组合键 + 单击启动器图标 – 或 – 应用程序窗口以升起当前视口上的所有窗口
这可能是最接近问题/评论中描述的选项。
假设我有一个凌乱的桌面,其中三个 nautilus 窗口埋在其他窗口下面。
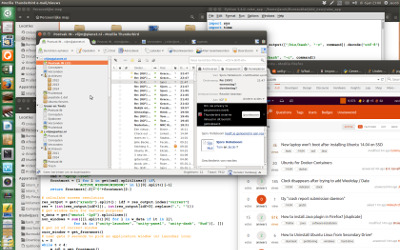
要升起所有 nautilus 窗口(示例快捷方式: Alt + 1 ):
-
按
Alt+1,松开(!) -
在 3 秒内,要么:\n单击启动器中的应用程序图标\n\n要么:\n单击应用程序的窗口之一\n\n结果:\n
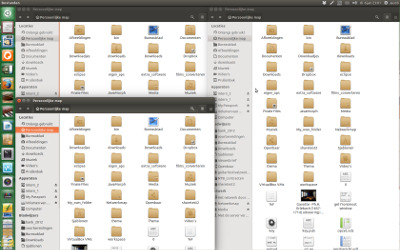
\n使用方法:
-
按照“如何使用”中的说明进行设置
-
Test-run 通过命令:
\n
raise_app\n -
如果一切正常,请将其添加到您选择的快捷键组合中:选择:系统设置> “Keyboard”> “Shortcuts”> “Custom Shortcuts”。单击 “+” 并添加命令
然后:
-
按组合键并在 3 秒内执行以下任一操作:\n
-
单击启动器中的应用程序图标
-
单击应用程序的窗口之一
-
剧本
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import subprocess
import getpass
import time
def get(command):
return subprocess.check_output(["/bin/bash", "-c", command]).decode("utf-8")
def execute(command):
subprocess.Popen(["/bin/bash", "-c", command])
def get_frontmost():
cmd = "xprop -root"
frontmost = [l for l in get(cmd).splitlines() if\
"ACTIVE_WINDOW(WINDOW)" in l][0].split()[-1]
return frontmost[:2]+"0"+frontmost[2:]
# calculate screen resolution
res_output = get("xrandr").split(); idf = res_output.index("current")
res = (int(res_output[idf+1]), int(res_output[idf+3].replace(",", "")))
# get window data for various purposes
w_data = get("wmctrl -lpG").splitlines()
non_windows = sum([[l.split()[0] for l in w_data if it in l]\
for it in ("unity-launcher", "unity-panel", "unity-dash", "Hud")], [])
# get id of current window
curr_window = get_frontmost()
# user gets 3 seconds to pick an application window (or launcher icon)
t = 0
while t < 4:
w_id1 = get_frontmost()
time.sleep(1)
w_id2 = get_frontmost()
if w_id1 == w_id2 or w_id2 in non_windows+[curr_window]:
t = t+1
else:
new_frontmost = w_id2
break
# raise
try:
pid = [l.split()[2] for l in w_data if new_frontmost in l]
wl_data = [l.split() for l in w_data]
raise_windows = [l[0] for l in wl_data if pid[0] == l[2] and\
0 < int(l[3]) < res[0] and 0 < int(l[4]) < res[1]]
[execute("wmctrl -ia "+item) for item in raise_windows]
except NameError:
pass
选项 4:组合键调用选项列表,显示当前视口上每个应用程序的窗口数量
事实证明,这比我想象的更方便:
按(再次示例)组合键 Alt + 1 调用 zenity 窗口,列出当前视口上的所有应用程序及其窗口数量:
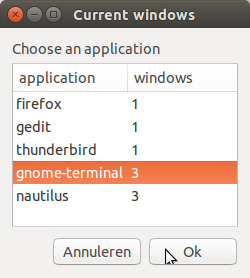
只需按 \u25b4 或 \u25be 箭头即可找到正确的选项。按 Enter,所选应用程序的所有窗口都会弹出。
如何使用:
-
按照“如何使用”中的说明进行设置
-
Test-run 通过命令:
\n
raise_app\n -
如果一切正常,请将其添加到您选择的快捷键组合中:选择:系统设置> “Keyboard”> “Shortcuts”> “Custom Shortcuts”。单击 “+” 并添加命令
剧本
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import subprocess
import getpass
def get(command):
return subprocess.check_output(["/bin/bash", "-c", command]).decode("utf-8")
def execute(command):
subprocess.Popen(["/bin/bash", "-c", command])
# calculate screen resolution
res_output = get("xrandr").split(); idf = res_output.index("current")
res = (int(res_output[idf+1]), int(res_output[idf+3].replace(",", "")))
# creating window list on current viewport / id's / application names
w_data = [l.split()[0:7] for l in get("wmctrl -lpG").splitlines()]
windows = [[get("ps -u "+getpass.getuser()+" | grep "+w[2]).split()[-1], w[0]]
for w in w_data if 0 < int(w[3]) < res[0] and 0 < int(w[4]) < res[1]]
# preparing zenity optionlist
apps = [item[0] for item in windows]
# prevent multiple zenity windows
if apps.count("zenity") > 1:
pass
elif apps.count("zenity") > 0:
execute('zenity --info --text "Another Zenity window is open already"')
# preventing empty windowlist
elif len(apps) > 0:
applist = [[app, str(apps.count(app))] for app in set(apps)]
applist.sort(key=lambda x: x[1])
# calling zenity window
try:
arg = get('zenity --list --text "Choose an application" '+\
'--title "Current windows" '+\
'--column "application" '+\
'--column "windows" '+\
'--height 250 '+\
'--width 250 '+\
(" ").join(sum(applist, [])))
except subprocess.CalledProcessError:
pass
# raise matching windows
try:
[execute("wmctrl -ia "+item[1]) \
for item in windows if arg.startswith(item[0])]
except (subprocess.CalledProcessError, NameError):
pass
else:
execute('zenity --info --text "No windows to list"')
选项 5:从启动器图标启动正在运行的应用程序的窗口
此选项存在一个启动器图标,其中当前正在运行的应用程序位于快速列表中。选择其中之一,应用程序的所有窗口都会升起。
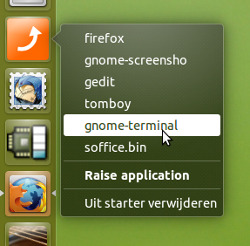
当正在运行的应用程序列表(在当前视口上)更改时,启动器会自动更新。快速列表在其他视口上显示不同的列表,其中打开其他应用程序的窗口(需要 1-2 秒适应)。
如前所述,虽然功能齐全,但此选项只是一个概念。它本身有一些外观上的小缺点。最重要的是:
-
执行操作后,光标 “wheel” 会持续旋转几秒钟。虽然它不影响功能,但它是一个美观的缺点。
-
正在运行的应用程序列表更改后,启动器图标中的应用程序列表需要 1-2 秒更新。
此外,设置稍微复杂一些(尽管下面详细解释):
如何使用
下面你会发现:
两个脚本/一个图标/一个 .desktop 文件\n
-
按照“如何使用”中的方式准备设置,将第一个(主)脚本保存为
~/bin中的raise_app -
将下面的图标另存为(右键另存为)为
raise.png\n
-
将
.desktop文件复制到一个空文件中,编辑该行\n
Icon=/path/to/raise.png\n\n
到图标的真实路径(引号之间有空格的路径)\n 将其另存为
~/.local/share/applications中的raise.desktop -
将
.desktop文件拖到启动器中添加 -
复制第二个脚本,将其粘贴到一个空文件中,将其另存为
~/bin中的update_apps,使其可执行。 -
将以下命令添加到启动应用程序(Dash > 启动应用程序 > 添加):
\n
update_apps\n -
注销并重新登录以使其正常工作。
第一个脚本
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import subprocess
import getpass
import sys
arg = sys.argv[1]
def get(command):
return subprocess.check_output(["/bin/bash", "-c", command]).decode("utf-8")
def execute(command):
subprocess.Popen(["/bin/bash", "-c", command])
# calculate screen resolution
res_output = get("xrandr").split(); idf = res_output.index("current")
res = (int(res_output[idf+1]), int(res_output[idf+3].replace(",", "")))
# creating window list on current viewport / id's / application names
w_data = [l.split()[0:7] for l in get("wmctrl -lpG").splitlines()]
windows = [[get("ps -u "+getpass.getuser()+" | grep "+w[2]).split()[-1], w[0]]
for w in w_data if 0 < int(w[3]) < res[0] and 0 < int(w[4]) < res[1]]
try:
[execute("wmctrl -ia "+item[1]) for item in windows if item[0].startswith(arg)]
except (subprocess.CalledProcessError, NameError):
pass
第二个脚本
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import subprocess
import getpass
import time
import os
dtfile = os.environ["HOME"]+"/.local/share/applications/raise.desktop"
def get(command):
return subprocess.check_output(["/bin/bash", "-c", command]).decode("utf-8")
def execute(command):
subprocess.Popen(["/bin/bash", "-c", command])
# calculate screen resolution
res_output = get("xrandr").split(); idf = res_output.index("current")
res = (int(res_output[idf+1]), int(res_output[idf+3].replace(",", "")))
# creating window list on current viewport / id's / application names
def applist():
try:
w_data = [l.split()[0:7] for l in get("wmctrl -lpG").splitlines()]
windows = [[get("ps -u "+getpass.getuser()+" | grep "+w[2]).split()[-1], w[0]]
for w in w_data if 0 < int(w[3]) < res[0] and 0 < int(w[4]) < res[1]]
except subprocess.CalledProcessError:
return []
else:
return set([app[0] for app in windows])
def update_dtfile(applications, text):
actionline = "Actions="+(";").join(applications)+";\n"
with open(dtfile) as src:
lines = src.readlines()
lines = lines[:[i for i in range(len(lines)) \
if lines[i].startswith("Actions=")][0]]+[actionline]
for item in text:
for it in item:
lines.append(it)
with open(dtfile, "wt") as out:
for line in lines:
out.write(line)
while True:
apps1 = applist()
time.sleep(1)
apps2 = applist()
if apps1 != apps2:
text = [["[Desktop Action "+it+"]\n", "Name="+it+"\n",
"Exec=raise_app "+it+"\n", "OnlyShowIn=Unity;\n\n",
]for it in apps2]
update_dtfile(apps2, text)
.desktop 文件
[Desktop Entry]
Name=Raise application windows
Comment=Raise groups of windows
Icon=/path/to/raise.png
Terminal=false
Type=Application
Version=1.0
Actions=
简要说明
上述所有解决方案都使用 wmctrl 创建窗口列表,使用 wmctrl -lpG 命令。该命令生成如下所示的行:
0x044000b3 0 3429 65 24 1615 1026 jacob-System-Product-Name unity - How to show all windows of an application? - Ask Ubuntu - Mozilla Firefox
这些行包括:
-
第一列:窗口的 id(我们可以用它来引发它)
-
第三列:拥有该窗口的 pid。
-
第 4 /5 列:窗口的几何图形 x-y (我们用它来查看窗口是否位于当前视口上,即
xrandr)
在 ps -u <username> 的输出中查找 pid,以获得应用程序的 “user-readable” 标识(名称)。\n因此我们可以为应用程序分配窗口。随后,我们可以使用命令 wmctrl -ia 在 for 循环中提升给定应用程序的窗口。
在选项 3 中,脚本启动一个 3 秒的 “waiting” 循环,重复使用 xprop -root 命令来查看最前面的窗口是否有任何变化;如果用户单击启动器图标以打开应用程序的窗口,或者直接单击窗口,就会发生这种情况。如果是,则 while 循环中断并查找 “new” 最前面的应用程序,然后引发该应用程序的所有其他窗口。
