问题描述
我知道更新存储库列表的命令是:
apt-get update
如何检查它是否在今天或过去 24 小时内被执行过?
我不知道我是否应该检查一些文件时间戳。或者发出另一个 apt 命令。或者使用 dpkg 实用程序。
在手册页中找不到有用的东西。
最佳回答
检查 /var/lib/apt/periodic/update-success-stamp 的时间戳。
$ ls -l /var/lib/apt/periodic/update-success-stamp
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 25 01:41 /var/lib/apt/periodic/update-success-stamp
这里的时间是 apt-get 最后一次执行时的 Jan 25 01:41。要仅获取时间,请在终端中使用以下命令,
$ ls -l /var/lib/apt/periodic/update-success-stamp | awk '{print $6" "$7" "$8}'
Jan 25 01:41
这是检查上次更新时间的最佳位置。如果您发现 /var/lib/apt/periodic/ 为空,您可以尝试,
ls -l /var/log/apt/history.log
更新
发现由于某些原因上述文件update-success-stamp或history.log在某些系统中仍然不可用。 derobert 中有一个新的 proposal 用于查看文件 /var/cache/apt/pkgcache.bin 。
pkgcache.bin 是 Apt 的内存映射包缓存位置。每次更新后都会更新。因此,知道 apt 上次更新的时间是完美的候选者。
可以使用以下命令来知道确切的时间,
ls -l /var/cache/apt/pkgcache.bin | cut -d' ' -f6,7,8
或者
stat /var/cache/apt/pkgcache.bin
次佳回答
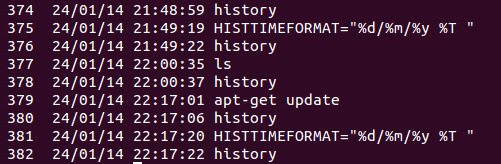
您可以在终端中检查您的命令历史记录:
history | grep 'apt update'
按时间检查:
HISTTIMEFORMAT="%d/%m/%y %T " history | grep '[a]pt update'
(正则表达式的 [a] 部分仅匹配字母 a,但在历史记录中 grepping 时具有不匹配自身的效果。)
第三种回答
我使用 /var/cache/apt 来确定是否需要运行 apt-get update 。默认情况下,如果 /var/cache/apt 的当前时间和缓存时间之间的差异小于 24 小时,我不需要运行 apt-get update 。可以通过将数字传递给函数 runAptGetUpdate() 来覆盖默认更新间隔
function trimString()
{
local -r string="${1}"
sed -e 's/^ *//g' -e 's/ *$//g' <<< "${string}"
}
function isEmptyString()
{
local -r string="${1}"
if [[ "$(trimString "${string}")" = '' ]]
then
echo 'true'
else
echo 'false'
fi
}
function info()
{
local -r message="${1}"
echo -e "\033[1;36m${message}\033[0m" 2>&1
}
function getLastAptGetUpdate()
{
local aptDate="$(stat -c %Y '/var/cache/apt')"
local nowDate="$(date +'%s')"
echo $((nowDate - aptDate))
}
function runAptGetUpdate()
{
local updateInterval="${1}"
local lastAptGetUpdate="$(getLastAptGetUpdate)"
if [[ "$(isEmptyString "${updateInterval}")" = 'true' ]]
then
# Default To 24 hours
updateInterval="$((24 * 60 * 60))"
fi
if [[ "${lastAptGetUpdate}" -gt "${updateInterval}" ]]
then
info "apt-get update"
apt-get update -m
else
local lastUpdate="$(date -u -d @"${lastAptGetUpdate}" +'%-Hh %-Mm %-Ss')"
info "\nSkip apt-get update because its last run was '${lastUpdate}' ago"
fi
}
示例输出:
<root@ubuntu><~/ubuntu-cookbooks/libraries>
# runAptGetUpdate
Skip apt-get update because its last run was '0h 37m 43s' ago
我从我的个人 github 中提取了这些函数:https://github.com/gdbtek/ubuntu-cookbooks/blob/master/libraries/util.bash
第四种回答
结合@ssokolow 的最后一条评论和来自 here 的答案,如果 apt-get update 在过去 7 天内没有运行,该命令将运行:
[ -z "$(find -H /var/lib/apt/lists -maxdepth 0 -mtime -7)" ] && sudo apt-get update
解释:
-
-mtime -7查找在过去 7 天内具有更改时间的文件。如果您关心更短的时间,可以使用-mmin。 -
-maxdepth 0确保 find 不会进入目录的内容。 -
如果
-H是软链接,则取消引用/var/lib/apt/lists -
如果由于某种原因
find失败,则该命令将运行。在我看来,这就像安全的默认设置。如果要翻转默认值,请在测试中使用-n,在查找命令中使用-mtime +7。
