问题描述
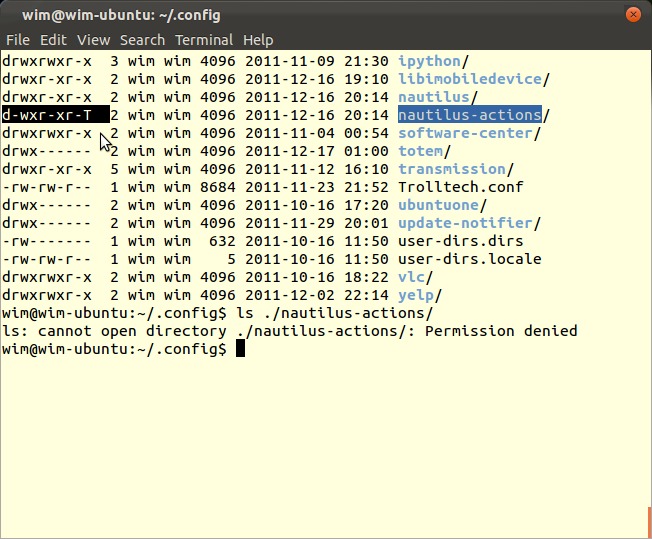
权限中的大写字母’T’是什么意思,它是如何工作的?这与我听说过但从未完全理解的’sticky bit’问题有关吗?
最佳方法
当未设置”others”的x位(即最后一个位置)时,大写的T出现。这两个目录都设置了粘滞位,但是第二个目录没有对”others”的执行权限
drwxrwxrwt 2 zanna zanna 4096 May 13 09:53 t
drwxrwxrwT 2 zanna zanna 4096 May 13 09:53 T
由于已由粘性位的[tT]代替,因此我们需要某种方式来知道目录是否具有对”others”的执行权限,因此区别对待
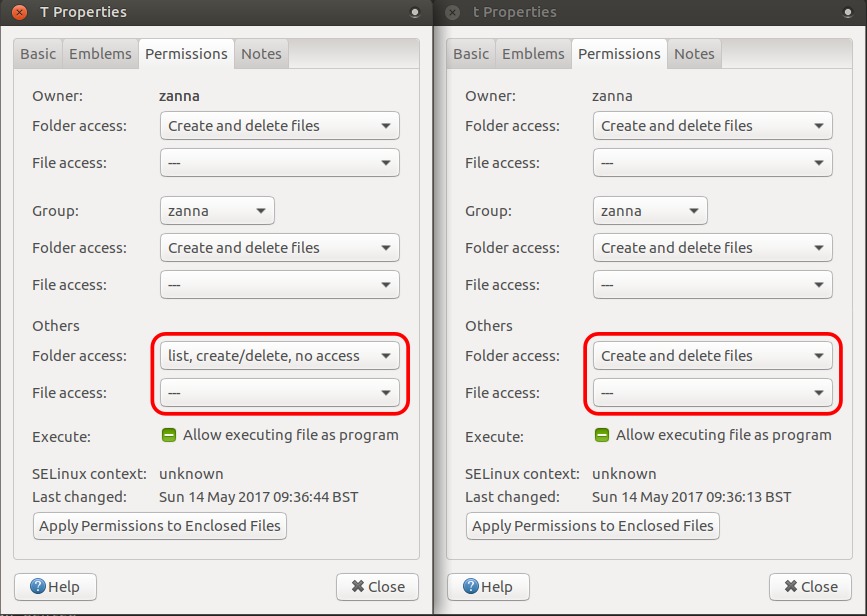
在我们的文件浏览器中,“属性”下的“权限”选项卡更清楚地显示具有和没有执行权限的目录之间的区别:我们需要执行权限才能访问(输入或统计)目录。
维基百科has to say关于目录上的粘滞位的内容:
The most common use of the sticky bit today is on directories. When the sticky bit is set, only the item’s owner, the directory’s owner, or the superuser can rename or delete files. Without the sticky bit set, any user with write and execute permissions for the directory can rename or delete contained files, regardless of owner. Typically this is set on the
/tmpdirectory to prevent ordinary users from deleting or moving other users’ files. This feature was introduced in 4.3BSD in 1986 and today it is found in most modern Unix systems.
